
设计模式-10-装饰器模式
个人github地址:HibisciDai
设计模式系列项目源码:HibisciDai/DesignPattern-LearningNotes-HibisciDai
processon在线UML类图:processon
[TOC]
设计模式-10-装饰器模式
装饰器模式(Decorator Pattern)
意图
动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责。
就增加功能来说装饰器模式相比生成子类更为灵活。
The Intent of this pattern is to add itional responsibilities dynamically to an object.
主要解决
一般的,我们为了扩展一个类经常使用继承方式实现,由于继承为类引入静态特征,并且随着扩展功能的增多,子类会很膨胀。
何时使用
在不想增加很多子类的情况下扩展类。
关键代码
- Component 类充当抽象角色,不应该具体实现。
- 修饰类引用和继承 Component 类,具体扩展类重写父类方法。
如何解决
将具体功能职责划分,同时继承装饰者模式。
应用实例
孙悟空有 72 变,当他变成”庙宇”后,他的根本还是一只猴子,但是他又有了庙宇的功能。
优点
装饰类和被装饰类可以独立发展,不会相互耦合,装饰模式是继承的一个替代模式,装饰模式可以动态扩展一个实现类的功能。
缺点
多层装饰比较复杂。
使用场景
注意事项
可代替继承。
动态撤销,扩展一个类的功能。
可以将装饰器视为一个退化的,仅有一个组件的组合。
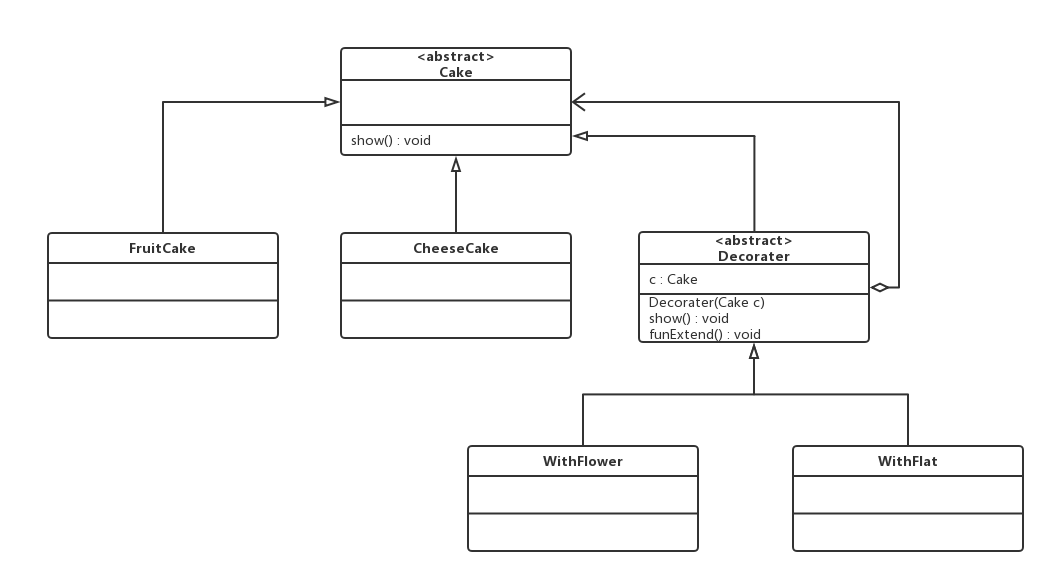
案例1
对于蛋糕,创建蛋糕与口味后进行装饰。
类图
代码
pattern10.decorator.demo1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
| public abstract class Cake {
abstract void show();
}
public class CheeseCake extends Cake {
@Override
void show() {
System.out.println("Here is CheeseCake");
}
}
public class FruitCake extends Cake {
@Override
void show() {
System.out.println("Here is FruitCake");
}
}
public abstract class Decorater extends Cake {
Cake c;
public Decorater(Cake c) {
super();
this.c = c;
}
@Override
void show() {
c.show();
funExtend();
}
abstract void funExtend();
}
public class WithFlower extends Decorater {
public WithFlower(Cake c) {
super(c);
}
@Override
void funExtend() {
System.out.println("WithFlower");
}
}
public class WithFlat extends Decorater {
public WithFlat(Cake c) {
super(c);
}
@Override
void funExtend() {
System.out.println("WithFlat");
}
}
|
测试输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cake c = new CheeseCake();
Decorater d = new WithFlat(c);
d.show();
}
}
|
1
2
| Here is CheeseCake
WithFlat
|
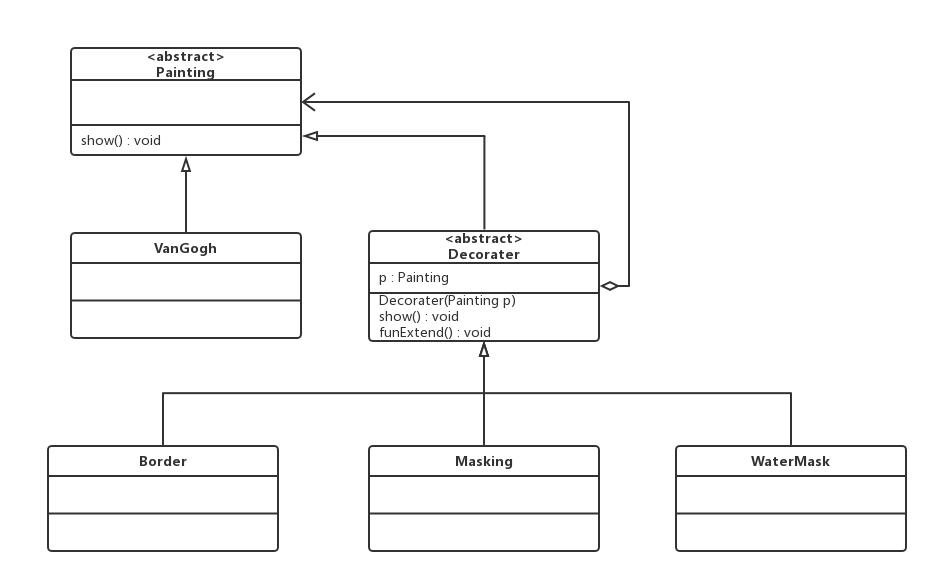
案例2
画刷画笔
类图
代码
pattern10.decorator.demo2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| public abstract class Painting {
abstract void show();
}
public class VanGogh extends Painting {
@Override
void show() {
System.out.println("Here is VanGogh");
}
}
public abstract class Decorater extends Painting {
Painting p;
public Decorater(Painting p) {
super();
this.p = p;
}
@Override
void show() {
p.show();
funExtend();
}
abstract void funExtend();
}
public class Border extends Decorater {
public Border(Painting p) {
super(p);
}
@Override
void funExtend() {
System.out.println("With Border");
}
}
public class Masking extends Decorater {
public Masking(Painting p) {
super(p);
}
@Override
void funExtend() {
System.out.println("With Masking");
}
}
public class WaterMask extends Decorater {
public WaterMask(Painting p) {
super(p);
}
@Override
void funExtend() {
System.out.println("With WaterMask");
}
}
|
测试输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Painting p = new VanGogh();
Decorater d = new Border(p);
d.show();
}
}
|
1
2
| Here is VanGogh
With Border
|



