人工智能实践-Tensorflow笔记-MOOC-第六讲循环神经网络
[TOC]
人工智能实践-Tensorflow笔记-MOOC-第六讲循环神经网络 通过脑记忆体提取历史数据的特征,预测出接下来最可能发生的情况。
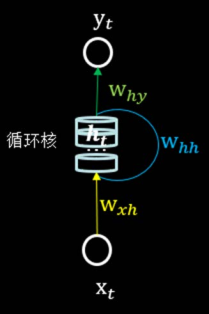
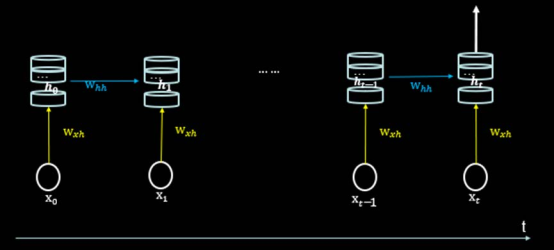
循环核 参数时间共享,循环层提取时间信息。
循环核具有记忆力,通过不同时刻的参数共享,实现了对时间序列的信息提取。
前向传播时:记忆体内存储的状态信息ht ,在每个时刻都被刷新,三个参数矩阵wxh whh why自始至终都是固定不变的。
可以设定记忆体个数,改变记忆体容量,当记忆体个数被指定,输入xt、输出yt维度被指定,周围这些待训练参数的维度也就被限定了。
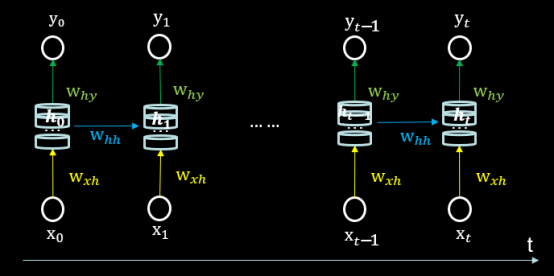
循环核时间步展开 按照时间步骤展开,就是把循环核按照时间轴方向展开,如下图所示。
每个时刻记忆体状态信息ht被刷新,记忆体周围的参数矩阵wxh、whh和why是固定不变的,我们训练优化的就是这些参数矩阵。
训练完成后,使用效果最好的参数矩阵,执行前向传播,输出预测结果。
人类脑中的记忆体每时每刻都根据当前的输入而更新,当前的预测推理,是根据你以往的知识积累,用固化下来的参数矩阵进行的推理判断,循环神经网络就是借助循环核实现的时间特征提取,再把提取到的信息送入全连接网络,实现连续数据的预测,yt是整个循环网络的末层,从公式来看,就是一个全连接网络,借助全连接网络,实现连续数据预测。
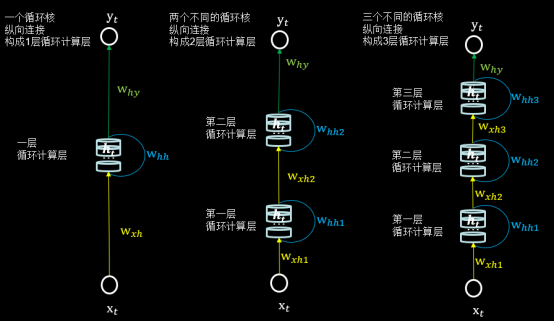
循环计算层 每个循环核构成一层循环计算层,循环计算层的层数是向输出方向增长的。
左图的网络有一个循环核,构成了一层循环计算层;
TF描述循环计算层 1 tf.keras.layers.SimpleRNN(记忆体个数, activation=‘激活函数’, return_sequences=是否每个时刻输出ht到下一层)
activation=‘激活函数’ (不写,默认使用tanh)
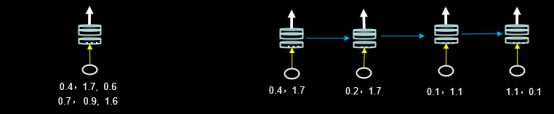
例: SimpleRNN(3, return_sequences=True),定义了一个具有三个记忆体的循环核,这个循环核会在每个时间步输出ht。
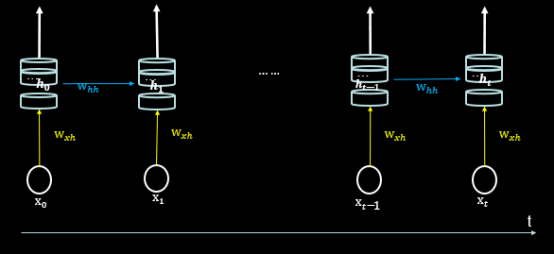
循环核在每个实践步输出ht,可以用这张图表示:
循环核仅在最后一个时间步输出ht,可以用这张图表示:
API对送入循环层的数据维度是有要求的,要求送入循环层的数据是三维的,第一维是送入样本的总数量,第二维是循环核按时间展开的步数,第三维是每个时间步输入特征的个数。
入RNN时, x_train维度:[送入样本数, 循环核时间展开步数, 每个时间步输入特征个数]
左图一共要送入RNN层两组数据,每组数据经过一个时间步就会得到输出结果,每个时间步送入三个数值,输入循环层的数据维度就是 [2, 1, 3] 。
右图只有一组数据,分四个时间步送入循环层,每个时间步送入输入两个数值,输入循环层的数据维度就是 [1, 4, 2] 。
循环计算过程I 字母预测:输入a预测出b,输入b预测出c,输入c预测出d,输入d预测出e,输入e预测出a。
神经网络的输入都是数字,所以我们先要把用到的 a b c d e 这五个字母,用数字表示出来,最简单直接的方法就是用独热码对这五个字母编码。
词向量空间
词向量空间
10000
a
01000
b
00100
c
00010
d
00001
e
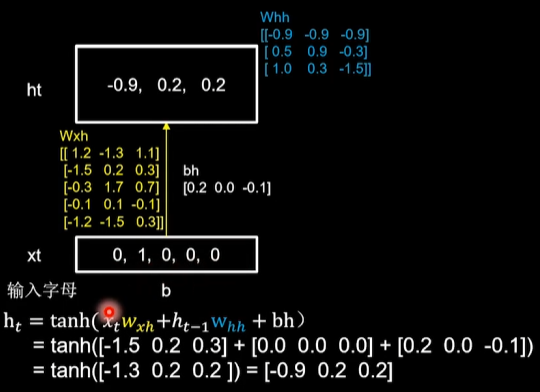
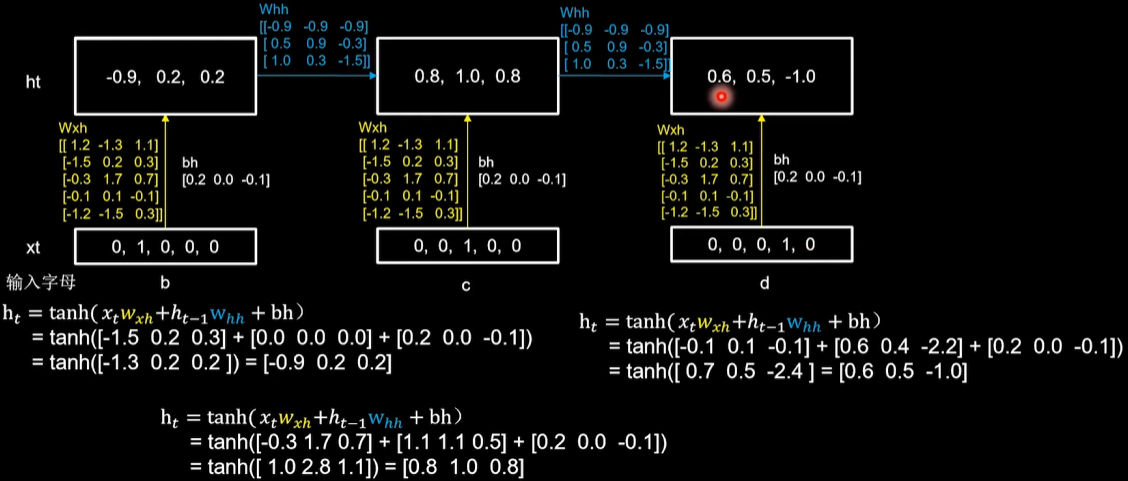
随机生成了Wxh、Whh和Why三个参数矩阵,记忆体的个数选取3,记忆体状态信息ht等于xt乘以wxh加上ht-1乘以whh加上bh,再过tanh激活函数。
当前输入xt[0, 1, 0, 0, 0]乘以黄色的参数矩阵wxh,得到[-2.3 0.8 1.1],上一时刻,也就是最开始时,记忆体状态信息等于0,所以这里加上0,再加上偏置矩阵bh,[0.5 0.3 -0.2],过tanh激活函数后,得到当前时刻的状态信息ht,记忆体存储状态信息被刷新为[-0.9 0.8 0.7]
这个过程可以认为脑中的记忆因为当前输入的事物而更新了。
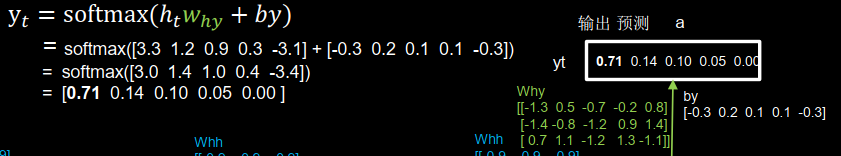
输出yt是把提取到的时间信息,通过全连接进行识别预测的过程,是整个网络的输出层。
用RNN实现输入一个字母,预测下一个字母(One hot 编码) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 import numpy as npimport tensorflow as tffrom tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, SimpleRNNimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport osinput_word = "abcde" w_to_id = {'a' : 0 , 'b' : 1 , 'c' : 2 , 'd' : 3 , 'e' : 4 } id_to_onehot = {0 : [1. , 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. ], 1 : [0. , 1. , 0. , 0. , 0. ], 2 : [0. , 0. , 1. , 0. , 0. ], 3 : [0. , 0. , 0. , 1. , 0. ], 4 : [0. , 0. , 0. , 0. , 1. ]} x_train = [id_to_onehot[w_to_id['a' ]], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['b' ]], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['c' ]], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['d' ]], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['e' ]]] y_train = [w_to_id['b' ], w_to_id['c' ], w_to_id['d' ], w_to_id['e' ], w_to_id['a' ]] np.random.seed(7 ) np.random.shuffle(x_train) np.random.seed(7 ) np.random.shuffle(y_train) tf.random.set_seed(7 ) x_train = np.reshape(x_train, (len (x_train), 1 , 5 )) y_train = np.array(y_train) model = tf.keras.Sequential([ SimpleRNN(3 ), Dense(5 , activation='softmax' ) ]) model.compile (optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.01 ), loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=False ), metrics=['sparse_categorical_accuracy' ]) checkpoint_save_path = "./checkpoint/rnn_onehot_1pre1.ckpt" if os.path.exists(checkpoint_save_path + '.index' ): print ('-------------load the model-----------------' ) model.load_weights(checkpoint_save_path) cp_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_save_path, save_weights_only=True , save_best_only=True , monitor='loss' ) history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32 , epochs=100 , callbacks=[cp_callback]) model.summary() file = open ('./weights.txt' , 'w' ) for v in model.trainable_variables: file.write(str (v.name) + '\n' ) file.write(str (v.shape) + '\n' ) file.write(str (v.numpy()) + '\n' ) file.close() acc = history.history['sparse_categorical_accuracy' ] loss = history.history['loss' ] plt.subplot(1 , 2 , 1 ) plt.plot(acc, label='Training Accuracy' ) plt.title('Training Accuracy' ) plt.legend() plt.subplot(1 , 2 , 2 ) plt.plot(loss, label='Training Loss' ) plt.title('Training Loss' ) plt.legend() plt.show() preNum = int (input ("input the number of test alphabet:" )) for i in range (preNum): alphabet1 = input ("input test alphabet:" ) alphabet = [id_to_onehot[w_to_id[alphabet1]]] alphabet = np.reshape(alphabet, (1 , 1 , 5 )) result = model.predict([alphabet]) pred = tf.argmax(result, axis=1 ) pred = int (pred) tf.print (alphabet1 + '->' + input_word[pred])
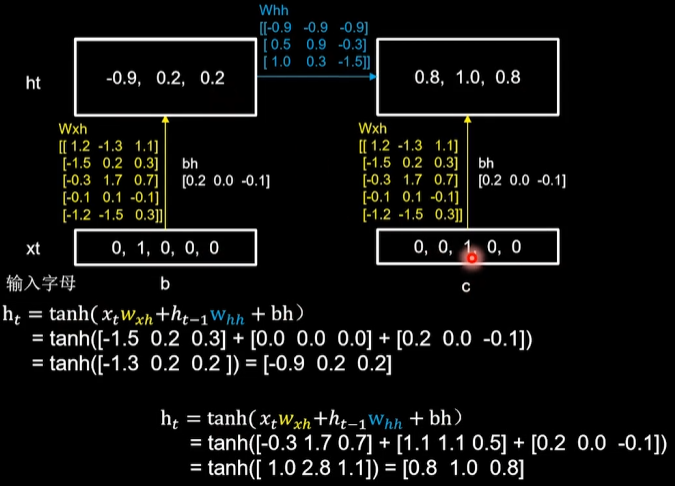
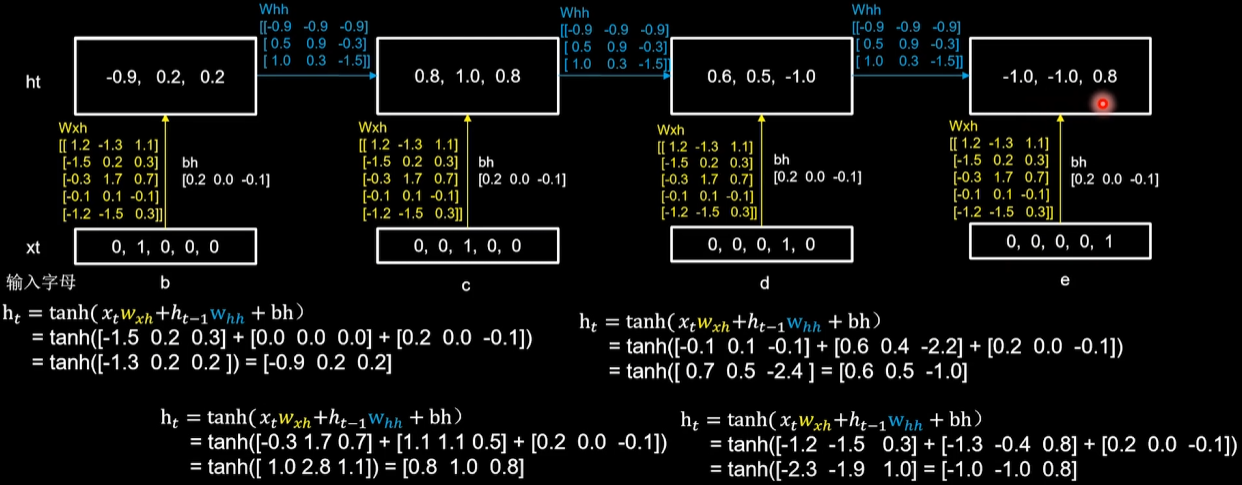
用RNN实现输入四个字母,预测下一个字母(One hot 编码) 每个时刻内,参数矩阵是固定的,记忆体会在每个时刻被更新。
第一个时刻:b输入[0, 1, 0, 0, 0],记忆体更新为[-0.9, 0.2, 0.2]
第二个时刻:c输入[0, 0, 1, 0, 0],记忆体更新[0.8, 1.0, 0.8]
第三个时刻:d输入[0, 0, 0, 1, 0],记忆体更新为[0.6, 0.5,- 1.0]
第四个时刻:e输入[0, 0, 0, 0, 1],记忆体更新为[-1.0, -1.0, 0.8]
四个时间步骤中,所用到的参数矩阵wxh核偏置项bh数值是相同的,输出预测通过全连接完成,带入yt计算公式,得到[0.71 0.14 0.10 0.05 0.00],输出预测结果为a。
因为输入的是e,下一个是e可能性最小。
代码 输入abcd输出e
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 import numpy as npimport tensorflow as tffrom tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, SimpleRNNimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport osinput_word = "abcde" w_to_id = {'a' : 0 , 'b' : 1 , 'c' : 2 , 'd' : 3 , 'e' : 4 } id_to_onehot = {0 : [1. , 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. ], 1 : [0. , 1. , 0. , 0. , 0. ], 2 : [0. , 0. , 1. , 0. , 0. ], 3 : [0. , 0. , 0. , 1. , 0. ], 4 : [0. , 0. , 0. , 0. , 1. ]} x_train = [ [id_to_onehot[w_to_id['a' ]], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['b' ]], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['c' ]], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['d' ]]], [id_to_onehot[w_to_id['b' ]], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['c' ]], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['d' ]], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['e' ]]], [id_to_onehot[w_to_id['c' ]], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['d' ]], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['e' ]], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['a' ]]], [id_to_onehot[w_to_id['d' ]], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['e' ]], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['a' ]], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['b' ]]], [id_to_onehot[w_to_id['e' ]], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['a' ]], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['b' ]], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['c' ]]], ] y_train = [w_to_id['e' ], w_to_id['a' ], w_to_id['b' ], w_to_id['c' ], w_to_id['d' ]] np.random.seed(7 ) np.random.shuffle(x_train) np.random.seed(7 ) np.random.shuffle(y_train) tf.random.set_seed(7 ) x_train = np.reshape(x_train, (len (x_train), 4 , 5 )) y_train = np.array(y_train) model = tf.keras.Sequential([ SimpleRNN(3 ), Dense(5 , activation='softmax' ) ]) model.compile (optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.01 ), loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=False ), metrics=['sparse_categorical_accuracy' ]) checkpoint_save_path = "./checkpoint/rnn_onehot_4pre1.ckpt" if os.path.exists(checkpoint_save_path + '.index' ): print ('-------------load the model-----------------' ) model.load_weights(checkpoint_save_path) cp_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_save_path, save_weights_only=True , save_best_only=True , monitor='loss' ) history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32 , epochs=100 , callbacks=[cp_callback]) model.summary() file = open ('./weights.txt' , 'w' ) for v in model.trainable_variables: file.write(str (v.name) + '\n' ) file.write(str (v.shape) + '\n' ) file.write(str (v.numpy()) + '\n' ) file.close() acc = history.history['sparse_categorical_accuracy' ] loss = history.history['loss' ] plt.subplot(1 , 2 , 1 ) plt.plot(acc, label='Training Accuracy' ) plt.title('Training Accuracy' ) plt.legend() plt.subplot(1 , 2 , 2 ) plt.plot(loss, label='Training Loss' ) plt.title('Training Loss' ) plt.legend() plt.show() preNum = int (input ("input the number of test alphabet:" )) for i in range (preNum): alphabet1 = input ("input test alphabet:" ) alphabet = [id_to_onehot[w_to_id[a]] for a in alphabet1] alphabet = np.reshape(alphabet, (1 , 4 , 5 )) result = model.predict([alphabet]) pred = tf.argmax(result, axis=1 ) pred = int (pred) tf.print (alphabet1 + '->' + input_word[pred])
Embedding-一种编码方法 独热码:数据量大 过于稀疏,映射之间是独立的,没有表现出关联性
Embedding:是一种单词编码方法,用低维向量实现了编码,这种编码通过神经网络训练优化,能表达出单词间的相关性。
tf.keras.layers.Embedding(词汇表大小, 编码维度)
编码维度就是用几个数字表达一个单词
对1-100进行编码, [4] 编码为 [0.25, 0.1, 0.11]tf.keras.layers.Embedding(100, 3)
入Embedding时, x_train维度:[送入样本数, 循环核时间展开步数]
用RNN实现输入一个字母,预测下一个字母(Embedding 编码) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 import numpy as npimport tensorflow as tffrom tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, SimpleRNN, Embeddingimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport osinput_word = "abcde" w_to_id = {'a' : 0 , 'b' : 1 , 'c' : 2 , 'd' : 3 , 'e' : 4 } x_train = [w_to_id['a' ], w_to_id['b' ], w_to_id['c' ], w_to_id['d' ], w_to_id['e' ]] y_train = [w_to_id['b' ], w_to_id['c' ], w_to_id['d' ], w_to_id['e' ], w_to_id['a' ]] np.random.seed(7 ) np.random.shuffle(x_train) np.random.seed(7 ) np.random.shuffle(y_train) tf.random.set_seed(7 ) x_train = np.reshape(x_train, (len (x_train), 1 )) y_train = np.array(y_train) model = tf.keras.Sequential([ Embedding(5 , 2 ), SimpleRNN(3 ), Dense(5 , activation='softmax' ) ]) model.compile (optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.01 ), loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=False ), metrics=['sparse_categorical_accuracy' ]) checkpoint_save_path = "./checkpoint/run_embedding_1pre1.ckpt" if os.path.exists(checkpoint_save_path + '.index' ): print ('-------------load the model-----------------' ) model.load_weights(checkpoint_save_path) cp_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_save_path, save_weights_only=True , save_best_only=True , monitor='loss' ) history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32 , epochs=100 , callbacks=[cp_callback]) model.summary() file = open ('./weights.txt' , 'w' ) for v in model.trainable_variables: file.write(str (v.name) + '\n' ) file.write(str (v.shape) + '\n' ) file.write(str (v.numpy()) + '\n' ) file.close() acc = history.history['sparse_categorical_accuracy' ] loss = history.history['loss' ] plt.subplot(1 , 2 , 1 ) plt.plot(acc, label='Training Accuracy' ) plt.title('Training Accuracy' ) plt.legend() plt.subplot(1 , 2 , 2 ) plt.plot(loss, label='Training Loss' ) plt.title('Training Loss' ) plt.legend() plt.show() preNum = int (input ("input the number of test alphabet:" )) for i in range (preNum): alphabet1 = input ("input test alphabet:" ) alphabet = [w_to_id[alphabet1]] alphabet = np.reshape(alphabet, (1 , 1 )) result = model.predict(alphabet) pred = tf.argmax(result, axis=1 ) pred = int (pred) tf.print (alphabet1 + '->' + input_word[pred])
用RNN实现输入四个字母,预测下一个字母(Embedding 编码) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 import numpy as npimport tensorflow as tffrom tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, SimpleRNN, Embeddingimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport osinput_word = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz" w_to_id = {'a' : 0 , 'b' : 1 , 'c' : 2 , 'd' : 3 , 'e' : 4 , 'f' : 5 , 'g' : 6 , 'h' : 7 , 'i' : 8 , 'j' : 9 , 'k' : 10 , 'l' : 11 , 'm' : 12 , 'n' : 13 , 'o' : 14 , 'p' : 15 , 'q' : 16 , 'r' : 17 , 's' : 18 , 't' : 19 , 'u' : 20 , 'v' : 21 , 'w' : 22 , 'x' : 23 , 'y' : 24 , 'z' : 25 } training_set_scaled = [0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 ] x_train = [] y_train = [] for i in range (4 , 26 ): x_train.append(training_set_scaled[i - 4 :i]) y_train.append(training_set_scaled[i]) np.random.seed(7 ) np.random.shuffle(x_train) np.random.seed(7 ) np.random.shuffle(y_train) tf.random.set_seed(7 ) x_train = np.reshape(x_train, (len (x_train), 4 )) y_train = np.array(y_train) model = tf.keras.Sequential([ Embedding(26 , 2 ), SimpleRNN(10 ), Dense(26 , activation='softmax' ) ]) model.compile (optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.01 ), loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=False ), metrics=['sparse_categorical_accuracy' ]) checkpoint_save_path = "./checkpoint/rnn_embedding_4pre1.ckpt" if os.path.exists(checkpoint_save_path + '.index' ): print ('-------------load the model-----------------' ) model.load_weights(checkpoint_save_path) cp_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_save_path, save_weights_only=True , save_best_only=True , monitor='loss' ) history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32 , epochs=100 , callbacks=[cp_callback]) model.summary() file = open ('./weights.txt' , 'w' ) for v in model.trainable_variables: file.write(str (v.name) + '\n' ) file.write(str (v.shape) + '\n' ) file.write(str (v.numpy()) + '\n' ) file.close() acc = history.history['sparse_categorical_accuracy' ] loss = history.history['loss' ] plt.subplot(1 , 2 , 1 ) plt.plot(acc, label='Training Accuracy' ) plt.title('Training Accuracy' ) plt.legend() plt.subplot(1 , 2 , 2 ) plt.plot(loss, label='Training Loss' ) plt.title('Training Loss' ) plt.legend() plt.show() preNum = int (input ("input the number of test alphabet:" )) for i in range (preNum): alphabet1 = input ("input test alphabet:" ) alphabet = [w_to_id[a] for a in alphabet1] alphabet = np.reshape(alphabet, (1 , 4 )) result = model.predict([alphabet]) pred = tf.argmax(result, axis=1 ) pred = int (pred) tf.print (alphabet1 + '->' + input_word[pred])
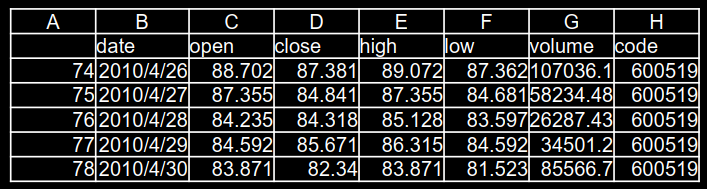
用RNN实现股票预测 贵州茅台股票数据,只使用C列数据
用连续60天开盘价预测第61天开盘价,使用以下代码下载真实数据:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 import tushare as tsimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltdf1 = ts.get_k_data('600519' , ktype='D' , start='2010-04-26' , end='2020-04-26' ) datapath1 = "./SH600519.csv" df1.to_csv(datapath1)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 import numpy as npimport tensorflow as tffrom tensorflow.keras.layers import Dropout, Dense, SimpleRNNimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport osimport pandas as pdfrom sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScalerfrom sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_errorimport mathmaotai = pd.read_csv('./SH600519.csv' ) training_set = maotai.iloc[0 :2426 - 300 , 2 :3 ].values test_set = maotai.iloc[2426 - 300 :, 2 :3 ].values sc = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0 , 1 )) training_set_scaled = sc.fit_transform(training_set) test_set = sc.transform(test_set) x_train = [] y_train = [] x_test = [] y_test = [] for i in range (60 , len (training_set_scaled)): x_train.append(training_set_scaled[i - 60 :i, 0 ]) y_train.append(training_set_scaled[i, 0 ]) np.random.seed(7 ) np.random.shuffle(x_train) np.random.seed(7 ) np.random.shuffle(y_train) tf.random.set_seed(7 ) x_train, y_train = np.array(x_train), np.array(y_train) x_train = np.reshape(x_train, (x_train.shape[0 ], 60 , 1 )) for i in range (60 , len (test_set)): x_test.append(test_set[i - 60 :i, 0 ]) y_test.append(test_set[i, 0 ]) x_test, y_test = np.array(x_test), np.array(y_test) x_test = np.reshape(x_test, (x_test.shape[0 ], 60 , 1 )) model = tf.keras.Sequential([ SimpleRNN(80 , return_sequences=True ), Dropout(0.2 ), SimpleRNN(100 ), Dropout(0.2 ), Dense(1 ) ]) model.compile (optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.001 ), loss='mean_squared_error' ) checkpoint_save_path = "./checkpoint/rnn_stock.ckpt" if os.path.exists(checkpoint_save_path + '.index' ): print ('-------------load the model-----------------' ) model.load_weights(checkpoint_save_path) cp_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_save_path, save_weights_only=True , save_best_only=True , monitor='val_loss' ) history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=64 , epochs=50 , validation_data=(x_test, y_test), validation_freq=1 , callbacks=[cp_callback]) model.summary() file = open ('./weights.txt' , 'w' ) for v in model.trainable_variables: file.write(str (v.name) + '\n' ) file.write(str (v.shape) + '\n' ) file.write(str (v.numpy()) + '\n' ) file.close() loss = history.history['loss' ] val_loss = history.history['val_loss' ] plt.plot(loss, label='Training Loss' ) plt.plot(val_loss, label='Validation Loss' ) plt.title('Training and Validation Loss' ) plt.legend() plt.show() predicted_stock_price = model.predict(x_test) predicted_stock_price = sc.inverse_transform(predicted_stock_price) real_stock_price = sc.inverse_transform(test_set[60 :]) plt.plot(real_stock_price, color='red' , label='MaoTai Stock Price' ) plt.plot(predicted_stock_price, color='blue' , label='Predicted MaoTai Stock Price' ) plt.title('MaoTai Stock Price Prediction' ) plt.xlabel('Time' ) plt.ylabel('MaoTai Stock Price' ) plt.legend() plt.show() mse = mean_squared_error(predicted_stock_price, real_stock_price) rmse = math.sqrt(mean_squared_error(predicted_stock_price, real_stock_price)) mae = mean_absolute_error(predicted_stock_price, real_stock_price) print ('均方误差: %.6f' % mse)print ('均方根误差: %.6f' % rmse)print ('平均绝对误差: %.6f' % mae)
用LSTM实现股票预测 传统RNN可以通过记忆体实现短期记忆进行连续数据的预测,当连续数据的序列变长时,会使展开时间步过长,在反向传播更新参数时,梯度要按照时间步连续相乘,会导致梯度消失。
LSTM 由Hochreiter & Schmidhuber 于1997年提出,通过门控单元改善了RNN长期依赖问题。
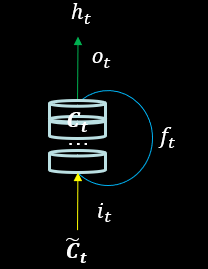
LSTM计算过程 LSTM 引入了三个门限:
遗忘门
输出门
引入了表征长期记忆的细胞态 $ C_{t} $
引入了等待存入长期记忆的候选态 $ \widetilde{C}_{t} $
三个门限都是当前时刻的输入特征 和上个时刻的短期记忆 的函数,分别表示为:
输入门(门限): , 决定了多少比例的信息会被存入当前细胞态;
遗忘门(门限): , 将细胞态中的信息选择性的遗忘;
输出门(门限): ,将细胞态中的信息选择性的进行输出;
三个公式中、 和 是待训练参数矩阵, 、 和 是待训练偏置项。 为 sigmoid 激活函数,它可以使门限的范围在 0 到 1 之间。
定义为记忆体,它表征短期记忆,是当前细胞态经过输出门得到的:
候选态表示归纳出的待存入细胞态的新知识, 是当前时刻的输入特征 和上个时刻的短期记忆 的函数:
细胞态 表示长期记忆, 它等于上个时刻的长期记忆 通过遗忘门的值和当前时刻归纳出的新知识 通过输入门的值之和:
当明确了这些概念, 这里举一个简单的例子理解一下 LSTM:
假设 LSTM 就是我们听老师讲课的过程, 目前老师讲到了第 45 页 PPT。我们的脑袋里记住的内容,是 PPT 第 1 页到第 45 页的长期记忆 。
它由两部分组成:一部分是 PPT 第 1 页到第 44 页的内容,也就是上一时刻的长期记忆 。我们不可能一字不差的记住全部内容,会不自觉地忘记了一些,所以上个时刻的长期记忆 要乘以遗忘门,这个乘积项就表示留存在我们脑中的对过去的记忆;另一部分是当前我们归纳出的新知识 ,它由老师正在讲的第 45 页 PPT(当前时刻的输入 ) 和第 44 页 PPT 的短期记忆留存(上一时刻的短期记忆 )组成。
将现在的记忆 乘以输入门后与过去的记忆一同存储为当前的长期记忆 。接下来,如果我们想把我们学到的知识(当前的长期记忆 )复述给朋友, 我们不可能一字不落的讲出来, 所以 需要经过输出门筛选后才成为了输出 。
当有多层循环网络时,第二层循环网络的输入 就是第一层循环网络的输出 ,即输入第二层网络的是第一层网络提取出的精华。 可以这么想, 老师现在扮演的就是第一层循环网络,每一页 PPT 都是老师从一篇一篇论文中提取出的精华,输出给我们。 作为第二层循环网络的我们,接收到的数据就是老师的长期记忆 过 tanh 激活函数后乘以输出门提取出的短期记忆 。
TF描述LSTM层 tf.keras.layers.LSTM(记忆体个数, return_sequences=是否返回输出)
return_sequences=True 各时间步输出ht
return_sequences=False 仅最后时间步输出ht(默认)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 model = tf.keras.Sequential([ LSTM(80 , return_sequences=True ), Dropout(0.2 ), LSTM(100 ), Dropout(0.2 ), Dense(1 ) ])
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 import numpy as npimport tensorflow as tffrom tensorflow.keras.layers import Dropout, Dense, LSTMimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport osimport pandas as pdfrom sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScalerfrom sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_errorimport mathmaotai = pd.read_csv('./SH600519.csv' ) training_set = maotai.iloc[0 :2426 - 300 , 2 :3 ].values test_set = maotai.iloc[2426 - 300 :, 2 :3 ].values sc = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0 , 1 )) training_set_scaled = sc.fit_transform(training_set) test_set = sc.transform(test_set) x_train = [] y_train = [] x_test = [] y_test = [] for i in range (60 , len (training_set_scaled)): x_train.append(training_set_scaled[i - 60 :i, 0 ]) y_train.append(training_set_scaled[i, 0 ]) np.random.seed(7 ) np.random.shuffle(x_train) np.random.seed(7 ) np.random.shuffle(y_train) tf.random.set_seed(7 ) x_train, y_train = np.array(x_train), np.array(y_train) x_train = np.reshape(x_train, (x_train.shape[0 ], 60 , 1 )) for i in range (60 , len (test_set)): x_test.append(test_set[i - 60 :i, 0 ]) y_test.append(test_set[i, 0 ]) x_test, y_test = np.array(x_test), np.array(y_test) x_test = np.reshape(x_test, (x_test.shape[0 ], 60 , 1 )) model = tf.keras.Sequential([ LSTM(80 , return_sequences=True ), Dropout(0.2 ), LSTM(100 ), Dropout(0.2 ), Dense(1 ) ]) model.compile (optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.001 ), loss='mean_squared_error' ) checkpoint_save_path = "./checkpoint/LSTM_stock.ckpt" if os.path.exists(checkpoint_save_path + '.index' ): print ('-------------load the model-----------------' ) model.load_weights(checkpoint_save_path) cp_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_save_path, save_weights_only=True , save_best_only=True , monitor='val_loss' ) history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=64 , epochs=50 , validation_data=(x_test, y_test), validation_freq=1 , callbacks=[cp_callback]) model.summary() file = open ('./weights.txt' , 'w' ) for v in model.trainable_variables: file.write(str (v.name) + '\n' ) file.write(str (v.shape) + '\n' ) file.write(str (v.numpy()) + '\n' ) file.close() loss = history.history['loss' ] val_loss = history.history['val_loss' ] plt.plot(loss, label='Training Loss' ) plt.plot(val_loss, label='Validation Loss' ) plt.title('Training and Validation Loss' ) plt.legend() plt.show() predicted_stock_price = model.predict(x_test) predicted_stock_price = sc.inverse_transform(predicted_stock_price) real_stock_price = sc.inverse_transform(test_set[60 :]) plt.plot(real_stock_price, color='red' , label='MaoTai Stock Price' ) plt.plot(predicted_stock_price, color='blue' , label='Predicted MaoTai Stock Price' ) plt.title('MaoTai Stock Price Prediction' ) plt.xlabel('Time' ) plt.ylabel('MaoTai Stock Price' ) plt.legend() plt.show() mse = mean_squared_error(predicted_stock_price, real_stock_price) rmse = math.sqrt(mean_squared_error(predicted_stock_price, real_stock_price)) mae = mean_absolute_error(predicted_stock_price, real_stock_price) print ('均方误差: %.6f' % mse)print ('均方根误差: %.6f' % rmse)print ('平均绝对误差: %.6f' % mae)
用GRU实现股票预测 GRU由Cho等人于2014年提出,优化LSTM结构。
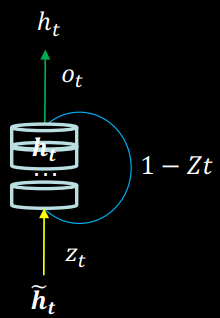
门控循环单元(Gated Recurrent Unit, GRU)是 LSTM 的一种变体,将 LSTM 中遗忘门与输入门合二为一为更新门,模型比 LSTM 模型更简单。
GRU 使记忆体 融合了长期记忆和短期记忆。 包含了过去信息 和现在信息(候选隐藏层) , 由更新门 分配重要性:
现在信息是过去信息 过重置门 与当前输入 共同决定的:
更新门和重置门的取值范围也是 0 到 1 之间:
TF描述GRU层 tf.keras.layers.GRU(记忆体个数, return_sequences=是否返回输出)
return_sequences=True 各时间步输出ht
return_sequences=False 仅最后时间步输出ht(默认)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 model = tf.keras.Sequential([ GRU(80 , return_sequences=True ), Dropout(0.2 ), LSTM(100 ), Dropout(0.2 ), Dense(1 ) ])
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 import numpy as npimport tensorflow as tffrom tensorflow.keras.layers import Dropout, Dense, GRUimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport osimport pandas as pdfrom sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScalerfrom sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_errorimport mathmaotai = pd.read_csv('./SH600519.csv' ) training_set = maotai.iloc[0 :2426 - 300 , 2 :3 ].values test_set = maotai.iloc[2426 - 300 :, 2 :3 ].values sc = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0 , 1 )) training_set_scaled = sc.fit_transform(training_set) test_set = sc.transform(test_set) x_train = [] y_train = [] x_test = [] y_test = [] for i in range (60 , len (training_set_scaled)): x_train.append(training_set_scaled[i - 60 :i, 0 ]) y_train.append(training_set_scaled[i, 0 ]) np.random.seed(7 ) np.random.shuffle(x_train) np.random.seed(7 ) np.random.shuffle(y_train) tf.random.set_seed(7 ) x_train, y_train = np.array(x_train), np.array(y_train) x_train = np.reshape(x_train, (x_train.shape[0 ], 60 , 1 )) for i in range (60 , len (test_set)): x_test.append(test_set[i - 60 :i, 0 ]) y_test.append(test_set[i, 0 ]) x_test, y_test = np.array(x_test), np.array(y_test) x_test = np.reshape(x_test, (x_test.shape[0 ], 60 , 1 )) model = tf.keras.Sequential([ GRU(80 , return_sequences=True ), Dropout(0.2 ), GRU(100 ), Dropout(0.2 ), Dense(1 ) ]) model.compile (optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.001 ), loss='mean_squared_error' ) checkpoint_save_path = "./checkpoint/stock.ckpt" if os.path.exists(checkpoint_save_path + '.index' ): print ('-------------load the model-----------------' ) model.load_weights(checkpoint_save_path) cp_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_save_path, save_weights_only=True , save_best_only=True , monitor='val_loss' ) history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=64 , epochs=50 , validation_data=(x_test, y_test), validation_freq=1 , callbacks=[cp_callback]) model.summary() file = open ('./weights.txt' , 'w' ) for v in model.trainable_variables: file.write(str (v.name) + '\n' ) file.write(str (v.shape) + '\n' ) file.write(str (v.numpy()) + '\n' ) file.close() loss = history.history['loss' ] val_loss = history.history['val_loss' ] plt.plot(loss, label='Training Loss' ) plt.plot(val_loss, label='Validation Loss' ) plt.title('Training and Validation Loss' ) plt.legend() plt.show() predicted_stock_price = model.predict(x_test) predicted_stock_price = sc.inverse_transform(predicted_stock_price) real_stock_price = sc.inverse_transform(test_set[60 :]) plt.plot(real_stock_price, color='red' , label='MaoTai Stock Price' ) plt.plot(predicted_stock_price, color='blue' , label='Predicted MaoTai Stock Price' ) plt.title('MaoTai Stock Price Prediction' ) plt.xlabel('Time' ) plt.ylabel('MaoTai Stock Price' ) plt.legend() plt.show() mse = mean_squared_error(predicted_stock_price, real_stock_price) rmse = math.sqrt(mean_squared_error(predicted_stock_price, real_stock_price)) mae = mean_absolute_error(predicted_stock_price, real_stock_price) print ('均方误差: %.6f' % mse)print ('均方根误差: %.6f' % rmse)print ('平均绝对误差: %.6f' % mae)